Houston Shockwave Therapy
Healing for chronic and acute injuries
Peroneal Nerve
Pain Relief
Inflammation Reversal
Collagen Synthesis
Shockwave Therapy for Peroneal Nerve
Houston Shockwave is a leading medical center that specializes in the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders using shockwave therapy. Our team of experienced medical professionals has successfully treated a wide range of conditions, including plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow, and Achilles tendonitis. We are proud to offer a revolutionary new treatment for patients suffering from peroneal nerve entrapment, a condition that can cause pain, weakness, and numbness in the foot and ankle.
What is Peroneal Nerve Entrapment?
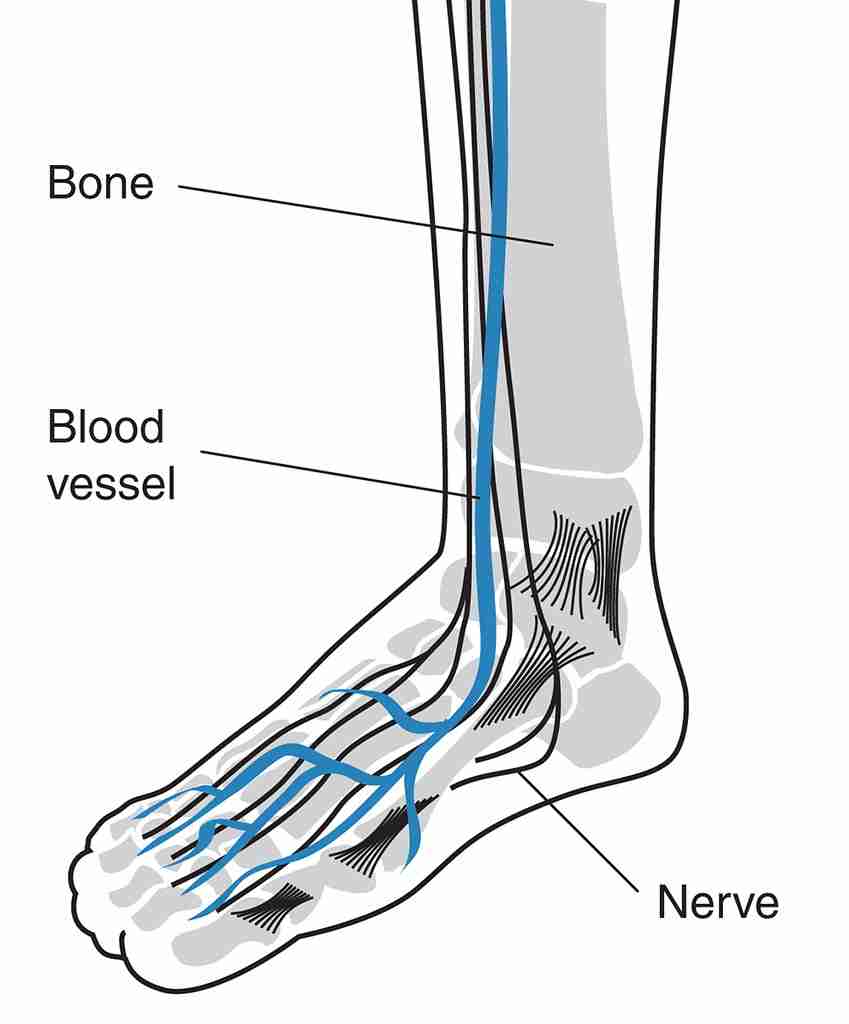
The peroneal nerve is a major nerve in the leg that runs down the outside of the knee and branches into two smaller nerves that control the muscles and sensations in the foot and ankle. Peroneal nerve entrapment occurs when the nerve becomes compressed or pinched, often due to pressure from surrounding tissues, such as muscles, tendons, or bones.
This can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Pain or discomfort on the outside of the foot or ankle
- Weakness or instability in the foot or ankle
- Numbness or tingling in the foot or ankle
- Difficulty lifting the foot or toes
Peroneal nerve entrapment can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, trauma, repetitive motion, or anatomical abnormalities. It is more common in athletes and people who engage in activities that involve repetitive or strenuous use of the legs, such as running, jumping, or cycling. It can also occur as a result of a direct blow or injury to the leg, such as a sprained ankle or a fracture.
Treatment Options for Peroneal Nerve Entrapment:
The treatment for peroneal nerve entrapment depends on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. In mild cases, conservative treatment options may be effective, such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), anti-inflammatory medications, or physical therapy. However, in more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to release the pressure on the nerve and restore normal function.
Shockwave Therapy for Peroneal Nerve Entrapment:
At Houston Shockwave, we offer a non-invasive and highly effective treatment option for peroneal nerve entrapment using shockwave therapy. Shockwave therapy is a cutting-edge technology that uses high-frequency sound waves to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes and promote tissue regeneration.
During a shockwave therapy session, a specialized machine delivers focused shockwaves directly to the affected area. The shockwaves penetrate deep into the tissue, breaking up scar tissue and calcifications, and increasing blood flow to the area. This stimulates the production of new collagen and other healing factors, leading to improved tissue quality and reduced pain and inflammation.
Shockwave therapy for peroneal nerve entrapment is a safe and effective alternative to surgery, with no downtime or recovery period. Patients can typically return to their normal activities immediately after treatment, and most experience significant pain relief and improved function within a few days.
Why Choose Houston Shockwave for Peroneal Nerve Treatment?
Houston Shockwave is a leader in the field of shockwave therapy for musculoskeletal disorders. Our team of medical professionals has extensive experience in treating a wide range of conditions, and we are dedicated to providing the highest quality care and personalized treatment plans for each of our patients.
When you choose Houston Shockwave for peroneal nerve treatment, you can expect:
- A comprehensive evaluation and diagnosis of your condition
- A customized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and goals
- State-of-the-art shockwave therapy technology and techniques
- Experienced and highly trained medical professionals
- A commitment to your health and wellbeing
Don’t let peroneal nerve entrapment hold you back from living your life to the fullest. Contact Houston Shockwave today to schedule a consultation